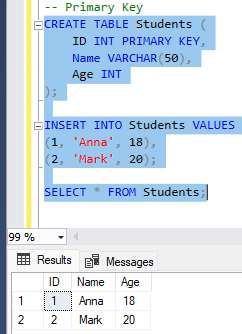
Primary and Foreign Keys
🔹 Primary Key
Selgitus: Primary Key määrab iga rea unikaalselt tabelis. Seda saab olla ainult üks.
CREATE TABLE Students (
ID INT PRIMARY KEY,
Name VARCHAR(50),
Age INT
);
INSERT INTO Students VALUES
(1, 'Anna', 18),
(2, 'Mark', 20);
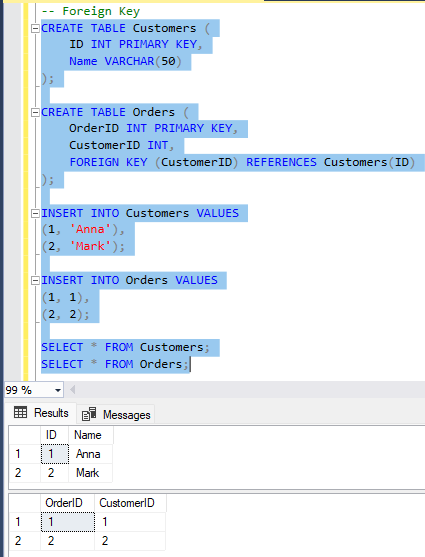
🔹 Foreign Key
Selgitus: Foreign Key viitab teise tabeli Primary Key-le ja ühendab tabelid omavahel.
CREATE TABLE Customers (
ID INT PRIMARY KEY,
Name VARCHAR(50)
);
CREATE TABLE Orders (
OrderID INT PRIMARY KEY,
CustomerID INT,
FOREIGN KEY (CustomerID) REFERENCES Customers(ID)
);
INSERT INTO Customers VALUES
(1, 'Anna'),
(2, 'Mark');
INSERT INTO Orders VALUES
(1, 1),
(2, 2);
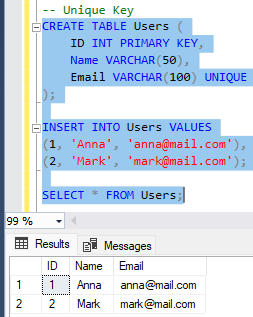
🔹 Unique Key
Selgitus: Unique Key tagab, et väärtused ei kordu, kuid neid võib olla mitu ühes tabelis.
CREATE TABLE Users (
ID INT PRIMARY KEY,
Name VARCHAR(50),
Email VARCHAR(100) UNIQUE
);
INSERT INTO Users VALUES
(1, 'Anna', 'anna@mail.com'),
(2, 'Mark', 'mark@mail.com');
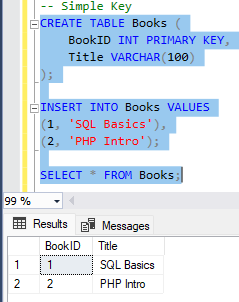
🔹 Simple Key
Selgitus: Simple Key koosneb ainult ühest veerust, mis on unikaalne.
CREATE TABLE Books (
BookID INT PRIMARY KEY,
Title VARCHAR(100)
);
INSERT INTO Books VALUES
(1, 'SQL Basics'),
(2, 'PHP Intro');
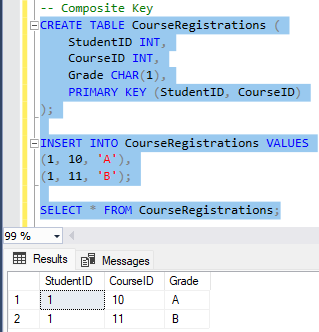
🔹 Composite Key
Selgitus: Composite Key koosneb mitmest veerust, mis üheskoos moodustavad unikaalse rea.
CREATE TABLE CourseRegistrations (
StudentID INT,
CourseID INT,
Grade CHAR(1),
PRIMARY KEY (StudentID, CourseID)
);
INSERT INTO CourseRegistrations VALUES
(1, 10, 'A'),
(1, 11, 'B');
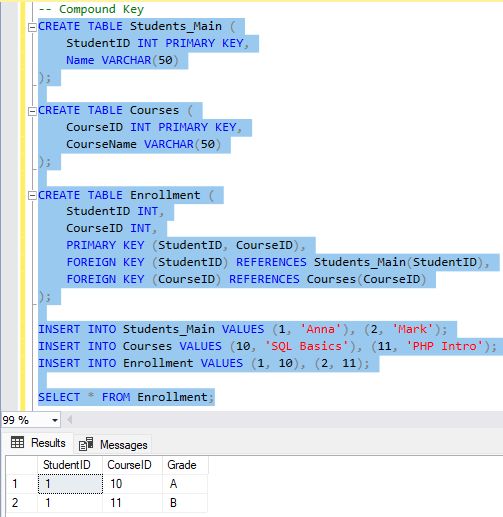
🔹 Compound Key
Selgitus: Compound Key on samuti mitmest veerust koosnev võti, kuid need veerud on samas ka Foreign Key’d teistes tabelites.
CREATE TABLE Students (
StudentID INT PRIMARY KEY,
Name VARCHAR(50)
);
CREATE TABLE Courses (
CourseID INT PRIMARY KEY,
CourseName VARCHAR(50)
);
CREATE TABLE Enrollment (
StudentID INT,
CourseID INT,
PRIMARY KEY (StudentID, CourseID),
FOREIGN KEY (StudentID) REFERENCES Students(StudentID),
FOREIGN KEY (CourseID) REFERENCES Courses(CourseID)
);
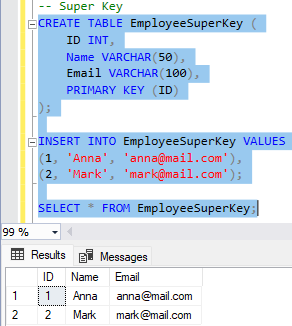
🔹 Super Key
Selgitus: Super Key on iga veergude kombinatsioon, mis määrab rea unikaalselt. Seal võib olla ka liigseid veerge.
CREATE TABLE EmployeeSuperKey (
ID INT,
Name VARCHAR(50),
Email VARCHAR(100),
PRIMARY KEY (ID)
);
-- Superkey’d: (ID), (Email), (ID, Name)
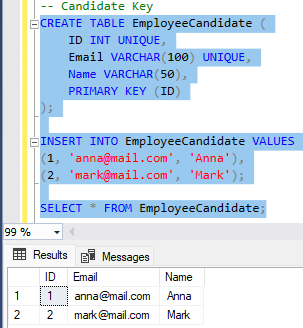
🔹 Candidate Key
Selgitus: Candidate Key on Super Key ilma liigsete veergudeta. Primary Key valitakse Candidate Key’de hulgast.
CREATE TABLE EmployeeCandidate (
ID INT UNIQUE,
Email VARCHAR(100) UNIQUE,
Name VARCHAR(50),
PRIMARY KEY (ID)
);
-- Candidate Keys: (ID), (Email)
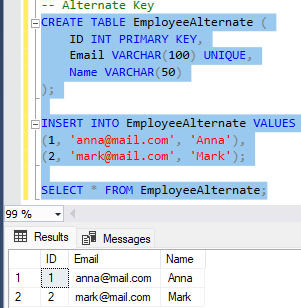
🔹 Alternate Key
Selgitus: Alternate Key on Candidate Key, mida ei valitud Primary Key’ks.
CREATE TABLE EmployeeAlternate (
ID INT PRIMARY KEY,
Email VARCHAR(100) UNIQUE,
Name VARCHAR(50)
);
-- Primary Key = ID
-- Alternate Key = Email
📚 Kasutatud allikad
Primary and Foreign Keys
Primary Key – A unique identifier for each and every record in the current database table.
Foreign Key – An identifier used to reference the primary key of a record in a different (“foreign”) table.
Let’s say we have a Users table, with UserId and Name columns; Name is a string, and UserId is a UUID
and the primary key. Because UserId is a primary key, each time we insert a new User, an ID will be generated for that user that is unique across all users— it can be used to reference that newly generated user anywhere in the system.
We also have a Posts table, with PostId, AuthorId, and Content columns; Content is a string, and PostId and AuthorId are both UUIDs. PostId would be a the primary key for the Posts table, and like UserId for Users, it is automatically generated every time a new post is created and is unique, allowing us to reference any post. AuthorId would hold the primary key of the user record associated with the user that authored the post. This allows us to look up the Name of an author of a post, without having to duplicate that data in the Posts table. AuthorId is a foreign key, because it points to a record in a different (Users) table.
You can have many foreign keys in a single table, since a single record might need to reference many other tables.
You don’t have to have a primary key on a table, but it is often helpful when you might need to reference a specific record in that table.
You can have multiple columns in a primary key (a compound primary key)

